1. What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is malicious software that infiltrates computers or networks, encrypts files and systems to make them unusable, and demands a ransom for recovery. The number of ransomware incidents has been rising in recent years; as of September 2025, there were 4,701 cases, a 34% increase compared to the previous year. Additionally, the median ransom demanded was $1.324 million, and the median amount actually paid was $1.0 million. Even though the amount actually paid was less than the sum demanded through negotiation, it still caused significant damage to the targeted companies. (Source: DeepStrike )When an attack occurs, it can halt business operations, and recently, secondary damage such as the leakage of personal or confidential information has become common, making this a serious issue. To minimize the impact of ransomware, it is essential not only to implement preventive measures but also to ensure rapid recovery after an incident. One effective recovery strategy is to maintain proper backups.
2. How to Back Up Data?
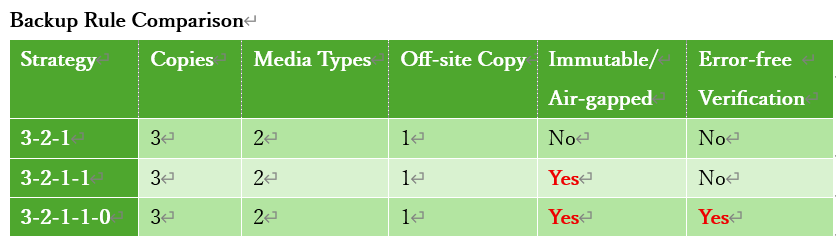
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) recommends the “3-2-1 Rule” for backups:- 3 – Keep 3 copies of any important file: 1 primary and 2 backups.
- 2 – Store the files on 2 different media types (e.g. cloud storage, network attached storage, and external storage devices) to protect against various hazards.
- 1 – Keep 1 copy offsite (e.g., outside your home or business facility)
Recently, variations such as the “3-2-1-1 Rule” and “3-2-1-1-0 Rule” have emerged:
- 3 – 2 – 1 – 1 Rule adds one immutable or air-gapped copy.
- 3 – 2 – 1 – 1 – 0 Rule further requires zero backup errors through verification.
Modern ransomware attacks often encrypt backups as well, so simply copying data is not enough. To minimize damage, it is recommended to design backups according to these rules. Which rule you should adopt depends on the impact of system downtime and the importance of confidential data.
Another critical point is verifying that recovery is actually possible. There are cases where backups exist, but recovery still fails due to poor procedures, forcing ransom payment. When designing backups, conduct Backup Training to confirm recovery capability. Measure recovery time and define RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) based on business continuity needs.
3.Summary
Ransomware is a growing cyber threat with severe potential consequences. To minimize damage, one key measure is to implement backups following recommended rules.If you would like to discuss ransomware countermeasures, including backup strategies, please contact us at the address below.
Contact | ID Europe B.V. (idnet.co.jp)
